Internal carotid artery occlusion motor deficits – Internal carotid artery occlusion (ICAO) motor deficits pose a formidable challenge in clinical practice. This article delves into the intricate relationship between ICAO and motor dysfunction, exploring the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic approaches, and management strategies associated with this condition.
ICAO, a blockage of the internal carotid artery, can result in a range of motor deficits due to impaired blood flow to the brain. These deficits can manifest in various forms, including weakness, paralysis, and coordination difficulties. Understanding the mechanisms underlying these motor deficits is crucial for effective diagnosis and management.
1. Definition and Pathophysiology
Definition
Internal carotid artery occlusion (ICAO) is a blockage of the internal carotid artery, one of the major arteries that supplies blood to the brain.
Pathophysiology
ICAO can be caused by various factors, including atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in the arteries), blood clots (thrombi), or emboli (pieces of debris that travel through the bloodstream).
When ICAO occurs, it can disrupt blood flow to the brain, leading to a lack of oxygen and nutrients in the affected brain tissue.
2. Motor Deficits Associated with ICAO
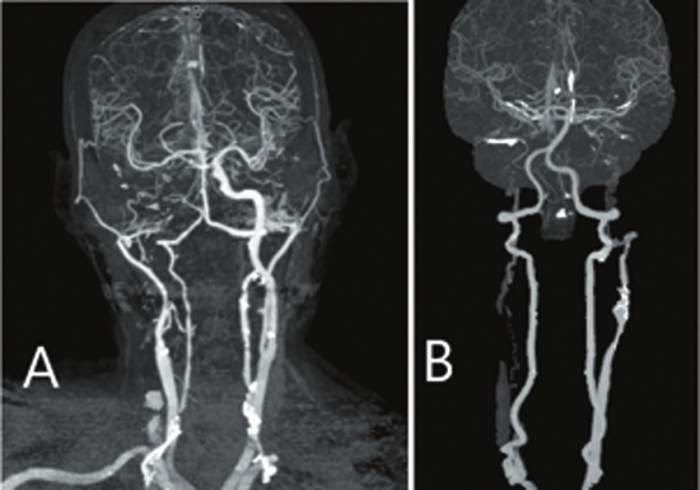
Common Motor Deficits
- Hemiparesis (weakness on one side of the body)
- Hemiplegia (paralysis on one side of the body)
- Dysarthria (difficulty speaking)
- Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
- Ataxia (impaired coordination and balance)
Mechanisms
These motor deficits arise due to damage to the brain areas responsible for motor control, such as the primary motor cortex and basal ganglia.
3. Diagnosis of ICAO
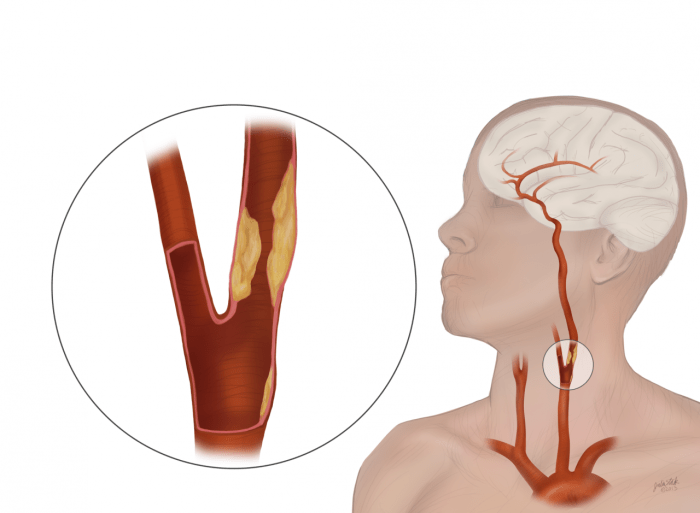
Clinical Presentation
Symptoms of ICAO can vary depending on the severity and location of the blockage.
Common symptoms include:
- Sudden onset of weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Difficulty speaking or swallowing
- Vision problems
- Confusion or memory loss
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) angiography can visualize the carotid arteries and detect any blockages.
4. Management of ICAO
Acute Management
Acute management of ICAO aims to restore blood flow to the brain as quickly as possible.
Treatment options include:
- Thrombolytic therapy (medications to dissolve blood clots)
- Endovascular interventions (procedures to remove or bypass the blockage)
Long-Term Management
Long-term management focuses on preventing further strokes and improving neurological function.
This includes:
- Lifestyle modifications (e.g., diet, exercise, smoking cessation)
- Medications (e.g., antiplatelets, anticoagulants)
- Rehabilitation (e.g., physical therapy, occupational therapy)
5. Prognosis and Outcomes: Internal Carotid Artery Occlusion Motor Deficits
Prognosis
The prognosis of ICAO patients depends on various factors, including the severity of the blockage, the location of the blockage, and the time to treatment.
Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
Complications
Potential complications of ICAO include:
- Stroke
- Cognitive impairment
- Seizures
6. Case Studies
Case Study 1
A 65-year-old male presented with sudden onset of right-sided weakness and difficulty speaking.
MRI revealed a left ICAO.
He underwent thrombectomy and made a good recovery, with minimal residual deficits.
Case Study 2
A 50-year-old female presented with a gradual onset of left-sided weakness over several months.
CT angiography revealed a right ICAO due to atherosclerosis.
She underwent carotid endarterectomy and had a favorable outcome.
7. Research and Emerging Therapies
Ongoing Research, Internal carotid artery occlusion motor deficits
Ongoing research in ICAO focuses on improving diagnostic techniques, developing new treatment strategies, and exploring the role of neuroprotective agents.
Emerging Therapies
Emerging therapies for ICAO include:
- Stem cell therapy
- Gene therapy
- Nanomedicine
These therapies aim to promote tissue repair, restore neurological function, and prevent further damage.
FAQ Compilation
What are the common motor deficits associated with ICAO?
Motor deficits associated with ICAO can include weakness or paralysis on one side of the body, difficulty with coordination and balance, and speech problems.
How is ICAO diagnosed?
ICAO is diagnosed based on a combination of clinical presentation and imaging studies, such as MRI or CT angiography, which can visualize the blocked artery.
What are the treatment options for ICAO?
Treatment options for ICAO include thrombolytic therapy to dissolve the clot, endovascular interventions to remove the blockage, and long-term management with rehabilitation and lifestyle modifications.