Includes creating compartments within a building with fire-resistive walls – The creation of compartments within buildings using fire-resistive walls plays a crucial role in enhancing fire safety. By dividing a structure into smaller, isolated sections, the spread of fire and smoke is effectively contained, safeguarding occupants and minimizing property damage.
Fire-resistive walls, with their exceptional resistance to fire, form the backbone of compartmentation systems. These walls are designed to withstand intense heat and flames for extended periods, preventing the fire from breaching compartment boundaries and endangering adjacent areas.
Building Compartmentation: Includes Creating Compartments Within A Building With Fire-resistive Walls
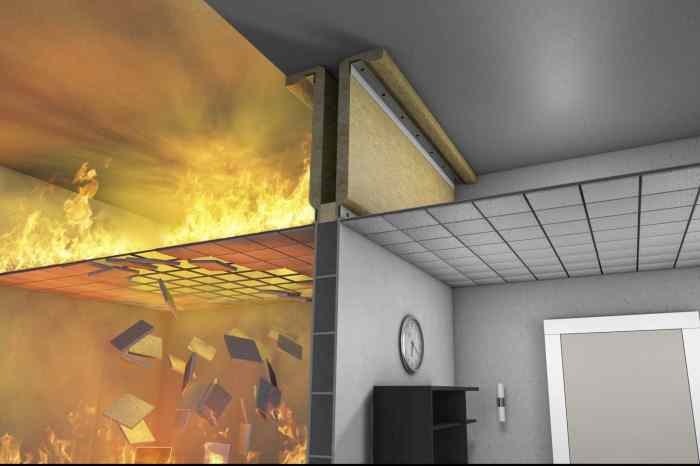

Building compartmentation involves dividing a structure into separate compartments using fire-resistive walls. This technique aims to limit the spread of fire and smoke within a building, enhancing fire safety and occupant protection.
Compartments can vary in size and purpose, including individual rooms, floors, or entire sections of a building. By creating compartments, the impact of a fire can be localized, preventing its rapid spread throughout the structure.
Types of Compartments
- Horizontal Compartments:Divide a building into floors or levels, limiting fire spread between floors.
- Vertical Compartments:Create vertical divisions within a building, such as separating different sections or wings.
- Atria Compartments:Enclose open spaces like atriums or courtyards to prevent smoke and heat accumulation.
Benefits of Compartmentation
- Reduced Fire Spread:Compartments act as barriers, containing fire and smoke within a localized area.
- Enhanced Occupant Safety:By limiting fire spread, compartmentation provides occupants with more time to evacuate and reduces exposure to smoke and heat.
- Property Protection:Compartmentation helps protect valuable assets and equipment by preventing the spread of fire to adjacent areas.
Fire-Resistive Walls
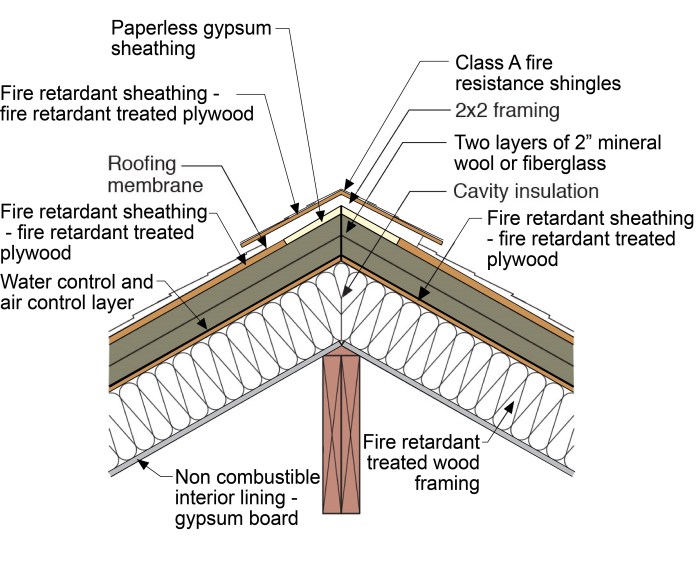
Fire-resistive walls are essential components of compartmentation systems. They are constructed from non-combustible materials and designed to resist the passage of fire and smoke for a specified period.
Types of Fire-Resistive Walls
- Load-Bearing Walls:Support the weight of the building while providing fire resistance.
- Non-Load-Bearing Walls:Do not support the building’s weight and are used primarily for fire separation.
- Curtain Walls:Non-structural walls that provide fire resistance while allowing for natural light and ventilation.
Fire Resistance Ratings
Fire resistance ratings indicate the amount of time a wall can withstand fire exposure without losing its structural integrity or allowing fire penetration. Ratings are typically measured in hours, with common ratings including 1 hour, 2 hours, and 4 hours.
Best Practices for Design and Installation
- Proper Material Selection:Use materials that meet fire resistance standards and are suitable for the intended application.
- Continuous Construction:Ensure walls are continuous from floor to ceiling, with no gaps or openings.
- Penetration Sealing:Seal any openings in walls, such as for pipes or electrical conduits, with fire-resistant materials.
- Fire Door Installation:Install fire doors that meet the same fire resistance rating as the wall and are self-closing.
Compartmentation Design
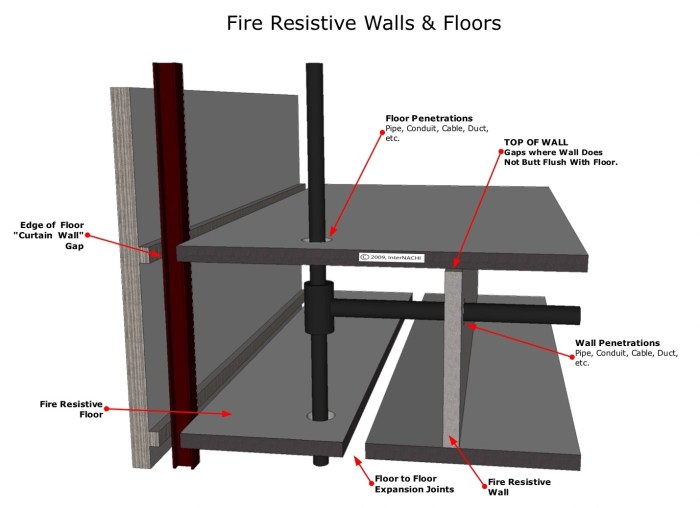
Effective compartmentation design requires careful consideration of several factors:
Size and Number of Compartments
The size and number of compartments should be determined based on the building’s occupancy, fire load, and evacuation strategy.
Balanced System
A balanced compartmentation system considers both fire safety and occupant safety. It should provide adequate fire containment while allowing for safe and efficient evacuation.
Evacuation Routes
Compartments should be designed to provide clear and unobstructed evacuation routes for occupants.
Compartmentation Maintenance
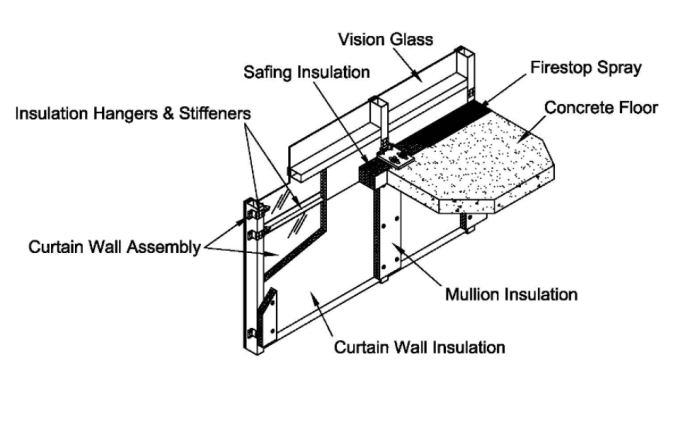
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of compartmentation systems:
Importance of Maintenance
Maintenance helps maintain the fire resistance of walls, ensures proper operation of fire doors, and prevents the accumulation of combustible materials.
Maintenance Tasks
- Visual Inspections:Check for any damage, gaps, or openings in walls and doors.
- Fire Door Testing:Verify that fire doors are self-closing and latching properly.
- Smoke Damper Inspection:Ensure smoke dampers are operating correctly and not obstructed.
- Penetration Sealing:Inspect and repair any damaged seals around penetrations in walls.
Maintenance Schedule, Includes creating compartments within a building with fire-resistive walls
Establish a regular schedule for maintenance and inspections to ensure ongoing effectiveness of the compartmentation system.
Clarifying Questions
What is the purpose of compartmentation in buildings?
Compartmentation aims to limit the spread of fire and smoke within a building, protecting occupants and minimizing property damage.
How do fire-resistive walls contribute to compartmentation?
Fire-resistive walls serve as barriers that prevent the passage of fire and smoke between compartments, maintaining the integrity of compartment boundaries.
What are the benefits of compartmentation?
Compartmentation enhances occupant safety by providing protected escape routes, reduces property damage by confining the fire to a smaller area, and facilitates firefighting operations by limiting the spread of smoke and flames.